Despite interest rate cut at 40-year low, EPF a dark horse – 5 reasons
epf interest rate 2021-22, EPF interest rate cut: The Employees’ Provident Fund Organization (EPFO), which is responsible for regulation and management of provident funds in the country, has reduced the interest rate on EPF to a 40-year low of 8.1 percent for the financial year 2021-22, allowing the more salaried class to benefit from such times. I am in pain when inflation is at an 8-year high. The interest rate for the financial year 2020-21 was 8.5 percent.
Though the announcement was made on May 3 after ratification by the central government, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman had strongly defended the Employees’ Provident Fund Organization (EPFO)’s decision to cut interest rates in March. He had said in the Rajya Sabha that the rate is determined by today’s realities where the interest rate on other small savings instruments was even lower. To make her point, Sitharaman referred to the returns on small savings schemes that provide safe and assured returns.
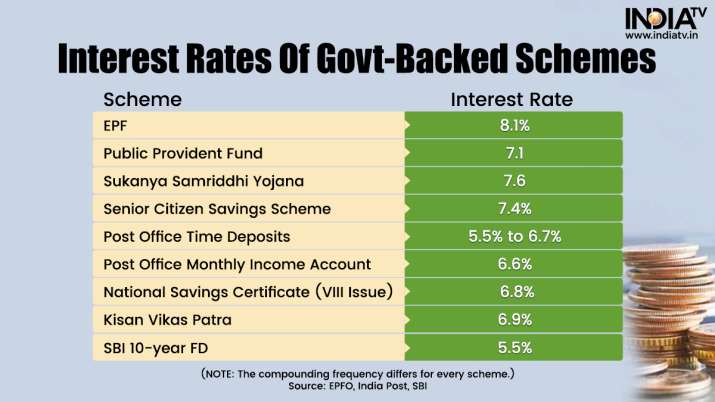
Sitharaman was absolutely right. A quick comparison between the government’s small savings schemes and the interest rate on EPF reveals that EPF is an attractive destination to park funds for a fixed return.
EPF vs PPF, SCSS
Schemes like Public Provident Fund (PPF), Sukanya Samriddhi, Senior Citizens Savings Scheme (SCSS), Ten Year Fixed Deposits of State Bank of India (SBI), Post Office Savings Schemes like Time Deposit Scheme (Similar to Bank FD), Monthly Income Scheme, Savings certificates like National Savings Certificate and Kisan Vikas Patra have stood the test of time and are considered as a safe way of investment. These schemes do not give quick returns, but in turn, they are safer (due to government backing) than the equity market linked schemes.
Interest rates of government backed schemes
It is worth mentioning here that the yield on 10-year government bonds is currently less than 7%.
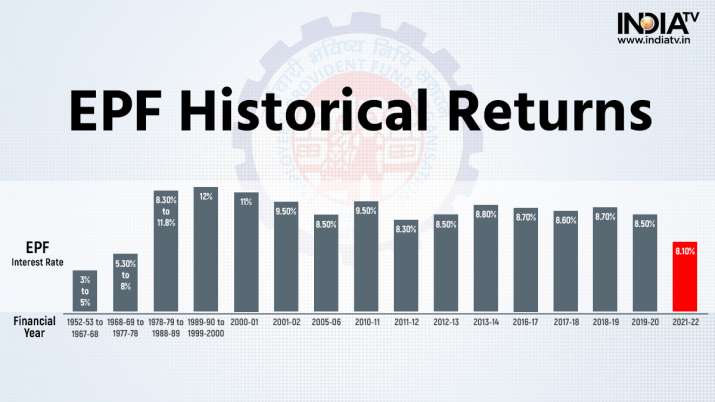
epf historical return
In the financial year 1952-53, the EPF interest rate was 3% which gradually increased to 8% in 1977-78 and then to 12% in 1991-92.
It is important to mention here that the EPF contribution also increased gradually since 1952-53, when 1 annas per rupee was payable by both the employee and the employer on the total basic salary, DA and food concession.
epf historical return
EPF remains the best bet – 5 reasons
1. Mandatory Clause
EPF contribution is mandatory for a salaried person. According to the rules, 12 percent of the basic salary and dearness allowance is deposited in the EPF account every month. You have no option here to stop the contribution. You save regularly regardless of your desire. This mandatory section allows EPF to score over other schemes.
This is a win-win for those making additional investments (more than 12%) in Voluntary Provident Fund (VPF).
2. Contribution
Contribution to EPF accounts is made by the employee as well as the employer. The employer directly deposits the amount into the EPF account of the employees on a monthly basis. While the employee contributes 12% of the basic pay and dearness allowance, the employer also contributes an equal part of the salary of the employees (8.33% for pension scheme and 3.67% for EPF). Accordingly, the total contribution to the EPF account becomes 24%.
3. Compound Interest
EPF interest is compounded annually. To make it simple, you earn interest on the interest you receive on contributions. Once again, this makes EPF an attractive destination for parking funds to get an attractive return.
Though interest is calculated every month, it is credited at the end of the financial year.
4. Tax Benefits
EPF also gives tax benefits! It is considered to be one of the most tax-efficient tools.
It has the status of Exempt, Exempt, Exempt (EEE). Here the contribution is deducted from the salary of the employee and no tax is applicable on the amount. Contribution can be claimed under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act. Also, the interest earned or maturity amount is absolutely tax free.
From 2021-22, the government introduced a clause whereby interest earned on EPF contribution above Rs 2.5 lakh is taxable.
Other government backed small savings schemes also offer tax benefits similar to EPF. But schemes like SCSS and FD are taxable.
5. Retirement
EPF is a traditional means of saving for retirement. In fact, it is a reliable retirement planning avenue. The more you contribute, the more you generate. In addition, you save tax in three stages – Contribution, Interest Accumulation and Withdrawal.
The entire amount can be withdrawn after retirement (withdrawals are allowed before retirement under certain conditions).
Where is the EPF contribution invested?
EPF is primarily a debt product. The money is mainly invested in debt products like government securities. In 2015, EPFO was allowed to start investing in equities, but with a limit. The statutory body was initially allowed only 5% exposure in equities. In 2017 the limit was raised to 15%.
Read more: Government approves 8.1% EPF interest rate for 2021-22, lowest in 40 years