Form of words:
wooAs the UN climate conference in Scotland highlights climate change policies and the impact of global warming, it is useful to understand what the science shows.
i am one atmospheric scientist who has worked on global climate science and assessment for most of my career. Here are six things you should know about the chart.
what is driving climate change
The primary focus of the talks is on carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas that results from the burning of fossil fuels – coal, oil and natural gas – as well as forest fires, land use changes and natural sources.
The Industrial Revolution of the late 1800s began a massive increase in the burning of fossil fuels. It powered homes, industries and opened up the planet to travel. same century, scientist Detected carbon dioxide potential To global temperature rise, which at the time was considered a potential benefit to the planet. Systematic measurements began in the mid-1900s and carbon dioxide has steadily increased Much of it is directly detectable for the combustion of fossil fuels.
Once in the atmosphere, carbon dioxide tends to stay there for a very long time. Part of the carbon dioxide released through human activities is taken up by plants, and some is directly absorbed into the ocean, but nearly half All of the carbon dioxide emitted by human activities remains in the atmosphere today – and it likely to be there for hundreds of yearsimpacting climate on a global scale.
During The first year of the pandemic in 2020When fewer people were driving and some industries closed for a while, carbon dioxide emissions from fuel dropped by about 6%. but this did not stop the increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide Because the amount released into the atmosphere by human activities is much more than what can be absorbed by nature.
If civilization today ceased its carbon dioxide emitting activities, it would still takes several hundred years Due to the long life of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere naturally drops enough to bring the planet’s carbon cycle back into balance.
Read also: COP26 is not just about India’s commitment to climate change. This is also a message for America
How do we know greenhouse gases can change the climate
Several lines of scientific evidence point to an increase in greenhouse emissions over the past century and a half as a driver of long-term climate change around the world. for example:
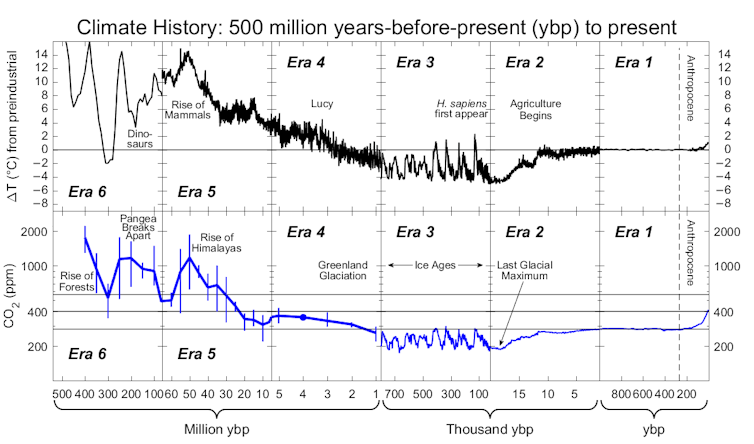
Based on Salavich et al., 2017, updated with data for the end of 2020, CC BY
- long-term record from ice cores, tree rings And coral Show that when the carbon dioxide level has been high, the temperature has also been high.
- Our neighboring planets also give evidence. Venus’s atmosphere is dense with carbon dioxide, and it is hottest planet As a result of this in our solar system, even though Mercury is closer to the Sun.
Temperatures are rising on every continent
Rising temperatures are evident in the records of every continent and ocean.
However, the temperature is not increasing at the same rate everywhere. A variety of factors affect local temperature, including land use which affects how much solar energy is absorbed or reflected, local heat sources such as urban heat island, and pollution.
The Arctic, for example, is warming three times faster than the global average Partly because as the planet warms, snow and ice melt, the surface is more likely to absorb, rather than reflect, the Sun’s radiation. As a result, ice cover and sea ice decrease even more rapidly.
Read also: ‘Our house is on fire’ in many ways. Climate change, Covid-19 ruining teenagers
What is climate change doing to the planet
Earth’s climate system is interconnected and complex, and even small temperature changes can have big effects – for example, with ice cover and sea level.
Changes are already happening. Studies show rising temperatures are already affected Precipitation, glaciers, weather patterns, tropical cyclone activity and severe storms. Many studies show that increase in frequencythe severity and duration of heat waves, for example, ecosystems, affect human life, commerce and agriculture.
The historical record of sea level has seen a mostly continuous rise over the past 150 years as glacier ice melts and rising temperatures cause ocean waters to expand, with some local deviations caused by sinking or rising land masses.
While extreme events are often caused by complex causes, some are exacerbated by climate change. Just as rising sea levels can make coastal flooding worse, heat waves are more damaging with higher baseline temperatures.
Climate scientists work hard to predict future changes as a result of carbon dioxide and other expected changes, such as an increase in world population. It is clear that there will be an increase in temperature and change in rainfall. The exact magnitude of change depends on several interacting factors.
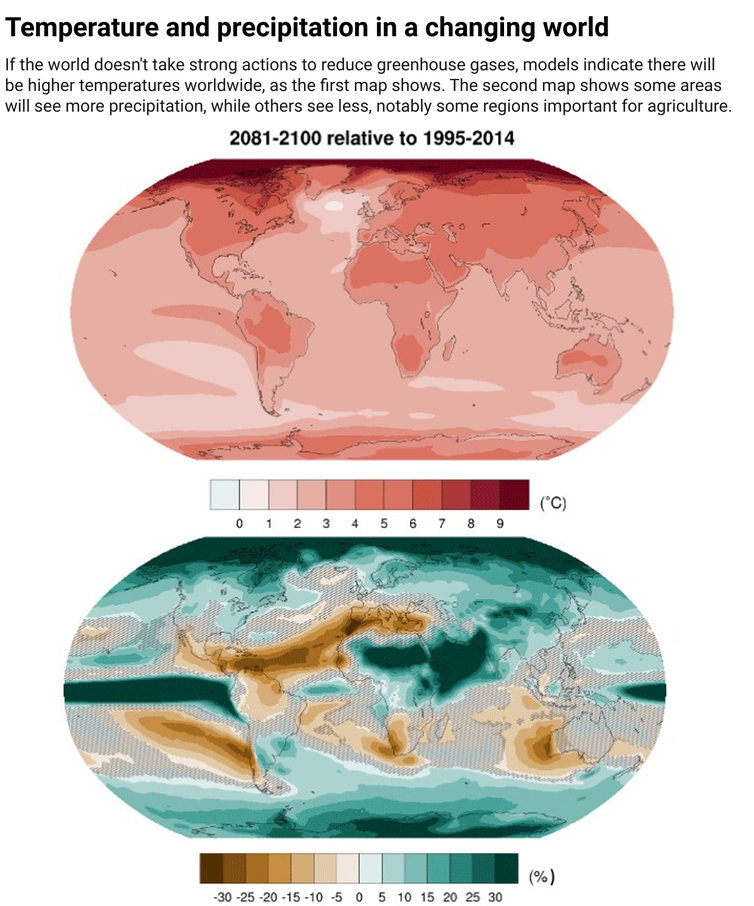
Claudia Tebaldi, et al., 2021
some reason to hope
On an optimistic note, scientific research is improving our understanding of climate and the complex Earth system, identifying the most vulnerable regions and guiding efforts to mitigate drivers of climate change. Work on renewable energy and alternative energy sources, as well as ways to capture carbon from industries or the wind, is creating more options for a better prepared society.
At the same time, people are learning about how they can reduce their own impact, with a growing understanding that a significant impact requires a globally coordinated effort. Electric vehicles, as well as solar and wind power, are on the rise At previously unimaginable rates. more people showing a willingness to adopt a new strategy To use energy more efficiently, to consume more sustainably and to choose renewable energy.
Scientists are increasingly recognizing that moving away from fossil fuels Additional Benefits, Including better air quality for human health and the ecosystem.
Betsy Weatherhead, senior scientist, University of Colorado Boulder
This article is republished from Conversation Under Creative Commons license. read the original article.
Read also: More floods, heatwaves, droughts – a 3℃ warmer world is worse than 1.5℃
subscribe our channel youtube And Wire
Why is the news media in crisis and how can you fix it?
India needs independent, unbiased, non-hyphenated and questionable journalism even more as it is facing many crises.
But the news media itself is in trouble. There have been brutal layoffs and pay-cuts. The best of journalism are shrinking, yielding to raw prime-time spectacle.
ThePrint has the finest young journalists, columnists and editors working for it. Smart and thinking people like you will have to pay a price to maintain this quality of journalism. Whether you live in India or abroad, you can Here.